The Pegasos is built using advanced chipsets available from VIA, Marvell,
and Sigmatel. These provide all of the advanced capabilities you will
find with the Pegasos.
Genesi uses the Discovery II from industry leader Marvell as the northbridge
in the Pegasos II. Marvell uses an advanced crossbar architecture, similar
to that found in advanced network routers. In addition, it provides:
ECC memory support, a general purpose high speed I/O for onboard logic,
gigabit ethernet fully capable of supplying the peak speed for this technology,
and up to 8-gigabytes of address space. The internal crossbar fabric supplies
up to 100 Gigabits/second, delivering unprecedented performance for the Pegasos II.
The Pegasos' audio codec is the Sigmatel STAC 9766 which supplies a 20-bit AC97
audio codec. It includes multiple input channels at 18-bit to allow for mixing
down a microphone, CD-audio and even DVD support. For modern audio, a digital
S/PDIF output has been included, allowing the Pegasos access to the latest
generation of audio technology.
VIA supplies many components for the Pegasos including the 8231 southbridge and
6306 controller. The 8231 supplies such things as the serial, parallel, IDE and
USB ports for the machine. The 6306 is a high performance IEEE-1394 controller
providing 3 Firewire® ports for the Pegasos to use.
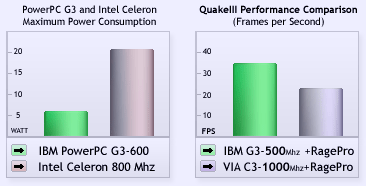
 The Pegasos ships with the PowerPC family of processors, either the IBM 750CXe (G3)
or the Motorola MPC7447 (G4). They bring many top end features to the Pegasos,
including:
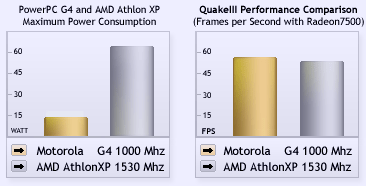
The Pegasos ships with the PowerPC family of processors, either the IBM 750CXe (G3)
or the Motorola MPC7447 (G4). They bring many top end features to the Pegasos,
including: